Blackjack, often referred to as "21," stands as one of the most popular and captivating casino card games worldwide. Its enduring appeal lies in its straightforward objective combined with elements of skill and strategy. Unlike pure games of chance, what are the rules of blackjack are fundamental to influencing your success. Understanding these rules is not just about knowing how to play; it's about making informed decisions that can reduce the house edge and significantly improve your chances of winning. This comprehensive guide will break down all the essential rules of blackjack, exploring the nuances of gameplay, player options, and various common rule variations you might encounter when you play blackjack online or at a traditional casino.
The Objective: Hit 21 (or Close to It)
The core objective of blackjack is simple: to have a hand total closer to 21 than the dealer's hand, without exceeding 21. If your hand goes over 21, you "bust" and automatically lose, regardless of the dealer's hand. If the dealer busts, all players who haven't busted win.

Card Values in Blackjack
Before you learn how to play blackjack, familiarizing yourself with the card values is crucial:
-
Numbered Cards (2-10): These cards are worth their face value (e.g., a 7 is 7 points, a 10 is 10 points).
-
Face Cards (Jack, Queen, King): All face cards are worth 10 points each.
-
Aces: An Ace is unique as it can be valued as either 1 or 11 points, depending on what best benefits the hand. This flexibility makes Aces powerful cards. A hand containing an Ace valued at 11 is called a "soft" hand (e.g., Ace-6 is a "soft 17"). If taking another card would make the total exceed 21, the Ace automatically reverts to a value of 1.
The Gameplay Flow

A typical blackjack game follows these steps:
-
Betting: Players place their wagers in the designated betting areas on the table.
-
Dealing the Cards: The dealer deals two cards to each player and two cards to themselves.
-
Player's Cards: Both of your cards are typically dealt face-up.
-
Dealer's Cards: One of the dealer's cards is dealt face-up (the "upcard"), and the other is dealt face-down (the "hole card").
-
Player's Turn: Starting from the player to the dealer's left, each player decides how to play their hand based on their two cards and the dealer's upcard. This is where strategic decisions come into play, utilizing the blackjack rules chart.
-
Dealer's Turn: After all players have completed their actions, the dealer reveals their hole card. The dealer must then hit or stand according to a predefined set of rules, which are typically printed on the table.
-
Dealer Must Hit: If the dealer's total is 16 or less, they must take another card.
-
Dealer Must Stand: If the dealer's total is 17 or more, they must stand (take no more cards).
-
Soft 17 Rule Variation: A common rule variation is whether the dealer hits or stands on a "soft 17" (an Ace and a 6). Some casinos mandate the dealer "hits on soft 17," which slightly increases the house edge. Others have the dealer "stands on soft 17," which is more favorable to the player. Always check this rule when learning how to play blackjack at casino.
-
Determining the Winner:
-
If your hand is closer to 21 than the dealer's (without busting), you win.
-
If the dealer busts, and you haven't, you win.
-
If your hand and the dealer's hand have the same total, it's a "push" or a "tie," and your bet is returned.
-
If the dealer's hand is closer to 21 than yours (and neither busted), you lose.
-
If you bust, you lose immediately.
Player Options in Blackjack

During your turn, you have several options to improve your hand:
-
Hit: Take an additional card from the dealer. You can hit in blackjack as many times as you like, as long as your hand doesn't exceed 21.
-
Stand: Take no more cards and end your turn. You "stand" when you are satisfied with your hand total.
-
Double Down: This powerful option allows you to double your initial bet in exchange for receiving exactly one more card. You can only double down in blackjack on your first two cards. It's generally recommended when you have a strong hand (e.g., 9, 10, or 11) and the dealer has a weak upcard.
-
Split: If your initial two cards are a pair (e.g., two 8s, two Queens), you can split in blackjack them into two separate hands. You must place an additional bet equal to your original wager for the new hand. Each hand is then played independently.
-
Important Split Rules:
-
Splitting Aces: When you split Aces, you typically receive only one additional card for each new hand. If you get a 10-value card on a split Ace, it counts as 21, not a blackjack, and usually pays even money.
-
Re-splitting: Some casinos allow you to re-split if you receive another pair after splitting.
-
Surrender (Optional Rule): Some blackjack tables offer the option to surrender in blackjack. If you feel your hand is very weak against the dealer's upcard, you can surrender and forfeit half of your original bet, rather than losing the entire amount.
-
Early Surrender: Allowed before the dealer checks for blackjack. (Rare)
-
Late Surrender: Allowed after the dealer checks for blackjack. (More common)
-
Semantic variation: blackjack surrender rules, when to surrender in blackjack
-
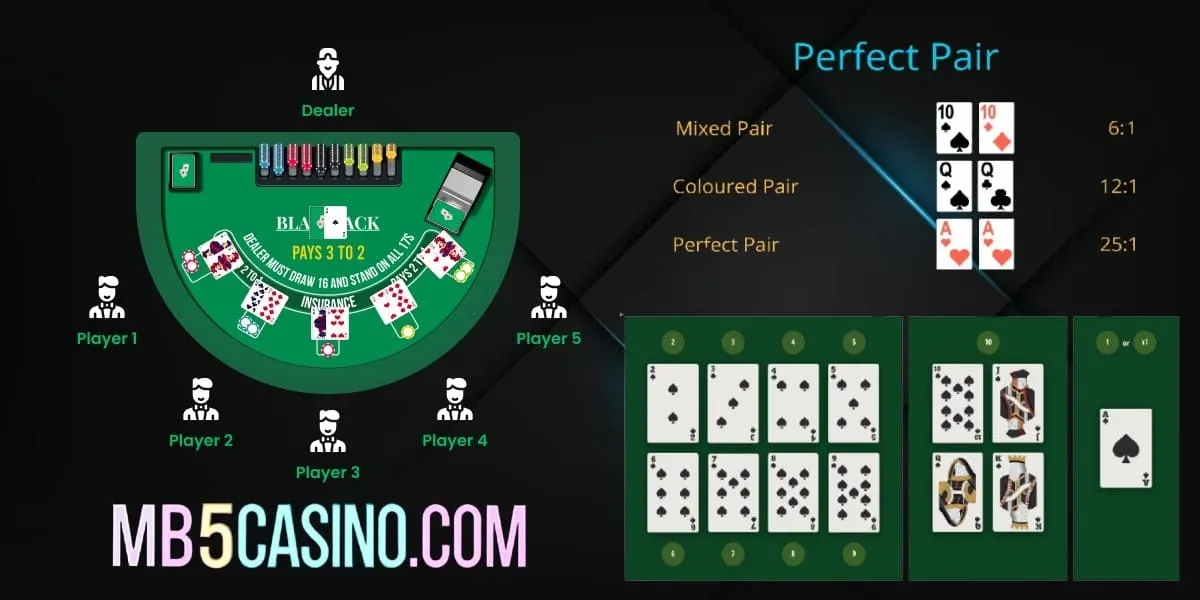
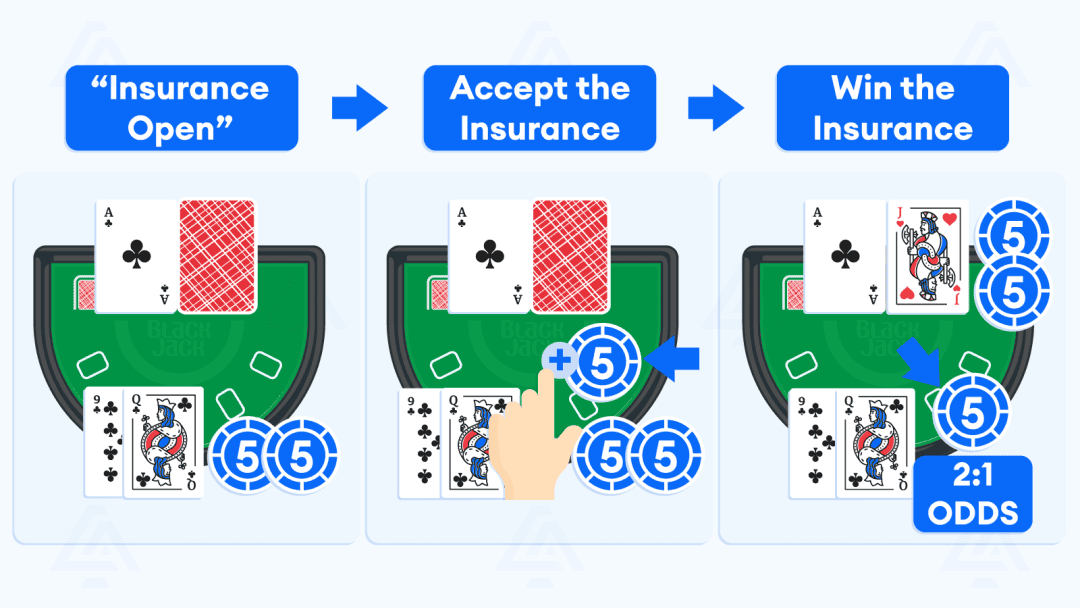
Insurance (Side Bet): If the dealer's upcard is an Ace, players are often offered "insurance." This is a side bet that the dealer has a blackjack (a 10-value card as their hole card). If you take insurance and the dealer does have blackjack, you win 2:1 on your insurance bet, effectively breaking even on the hand. However, blackjack insurance rules dictate that this is generally considered a bad bet for players in the long run, as the odds are not in your favor.
Understanding Blackjack Insurance: Rules and Rationale
Blackjack insurance is one of the most frequently misunderstood, and often misused, side bets in the game. It's crucial for any player, from beginner to experienced, to grasp its rules and, more importantly, its true value.
Blackjack Insurance Bet Rules: What is it and How Does it Work?
When the dealer's upcard is an Ace, players are offered the option to place an "insurance" bet. This is a side bet that is entirely separate from your main wager.
-
The Proposition: You are essentially betting that the dealer's face-down card (the "hole card") is a 10-value card (10, Jack, Queen, or King), which would give the dealer a blackjack (a natural 21).
-
Bet Amount: The insurance bet rules typically state that you can wager up to half of your original bet amount. For instance, if your main bet is $20, you can place an insurance bet of up to $10.
-
Payout: If the dealer indeed has a blackjack, your insurance bet pays out at 2:1 odds.
-
Outcome if Dealer Has Blackjack:
-
You win your insurance bet (e.g., $10 insurance bet wins $20).
-
You lose your original bet (since the dealer's blackjack beats your hand, unless you also have a blackjack).
-
The net effect is that you break even on the hand. For example, if your original bet was $20 and you took $10 insurance: you lose $20 on your main bet, but win $20 ($10 * 2) on your insurance, resulting in a net loss/win of $0.
-
Outcome if Dealer Does NOT Have Blackjack:
-
You lose your insurance bet.
-
The main hand continues as normal, and you play it out against the dealer's total.
-
In this scenario, you've lost the insurance bet in addition to whatever happens with your main hand.
"Even Money" – A Special Case of Insurance
Sometimes, when you have a blackjack yourself and the dealer's upcard is an Ace, the dealer might ask if you want "even money." This is essentially the same as taking an insurance bet when you have a blackjack.
-
If you take "even money," you immediately get paid 1:1 on your blackjack (e.g., a $20 blackjack pays $20 profit) regardless of whether the dealer has blackjack or not.
-
If you don't take even money (which is the same as refusing insurance in this scenario), your blackjack usually pays 3:2. If the dealer also has blackjack, it's a push (you get your original bet back). If the dealer doesn't have blackjack, you get the full 3:2 payout.
Mathematically, taking "even money" is the same as taking insurance when you have a blackjack and the dealer shows an Ace. Both are generally considered poor decisions for a basic strategy player.
Is Blackjack Insurance a Good Bet? The Mathematical Verdict
This is the million-dollar question, and for the vast majority of players, the answer is a resounding NO. Blackjack insurance is generally considered a bad bet.
Here's why:
-
High House Edge: The primary reason insurance is a poor bet is its inherently high house edge. While the main blackjack game, when played with basic strategy, can have a house edge of less than 1% (often around 0.5%), the house edge on the insurance bet typically ranges from 5.8% to over 7%, depending on the number of decks used. This is significantly higher than most other bets in the casino.
-
Unfavorable Odds: When the dealer shows an Ace, what are the odds that their hole card will be a 10-value card?
-
In a standard multi-deck game, there are 16 cards (10s, Js, Qs, Ks) out of 52 total cards in a deck.
-
After the deal, with the dealer's Ace showing and your two cards, there are 50 cards remaining, and roughly 16 of them are 10-value cards.
-
This means the probability of the dealer having a blackjack is approximately 30.7% to 31.5% (roughly 1 in 3).
-
However, the insurance bet pays 2:1. For the bet to be break-even, the probability of the dealer having a blackjack would need to be exactly 1 in 3 (33.3%). Since the actual probability is less than that, the casino has a built-in advantage. You are simply not being paid enough for the risk you are taking.
-
Does Not Protect Your Original Bet: The name "insurance" is misleading. It doesn't actually "insure" or protect your original bet from being lost if the dealer has blackjack. Instead, it's a separate wager that allows you to break even if the dealer has blackjack. If the dealer doesn't have blackjack, you lose the insurance bet outright, potentially adding to your losses.
-
Impact on Bankroll: Consistently making insurance bets will, over time, erode your bankroll faster due to the high house edge. It's a drain on your funds that detracts from the main game's favorable odds.
-
Distraction from Basic Strategy: Focusing on side bets like insurance can distract players from adhering to proper blackjack basic strategy, which is the mathematically correct way to play every hand and minimize the house edge.
Special Situations and Payouts
-
Blackjack (Natural 21): If your first two cards are an Ace and any 10-value card (a total of 21), you have a blackjack. This usually pays out at 3:2 odds (e.g., a $10 bet wins $15), unless the dealer also has a blackjack, resulting in a push. If the casino offers a 6:5 payout for blackjack, avoid it, as it significantly increases the house edge.
-
Dealer Blackjack: If the dealer's upcard is a 10 or Ace and their hole card gives them 21, they immediately win (unless you also have blackjack, resulting in a push).
Common Blackjack Rule Variations
It's crucial to be aware that blackjack table rules can vary slightly from one casino to another, or even between different tables within the same online casino. These variations impact the house edge:
-
Number of Decks: Games are typically played with 1 to 8 decks. Fewer decks generally reduce the house edge.
-
Dealer Hits/Stands on Soft 17: As mentioned, this is a significant rule to check.
-
Payout for Blackjack: 3:2 is standard and favorable; avoid 6:5.
-
Re-splitting Aces: Some casinos don't allow re-splitting Aces after the initial split.
-
Doubling After Split: Some casinos restrict doubling down after splitting a hand.
-
Surrender Option: Not always available.
When you find blackjack rules for a specific game, always take a moment to understand these variations.
Why Knowing the Rules Matters
Understanding what are the rules of blackjack is the first step towards playing effectively. It empowers you to:
-
Make Optimal Decisions: Knowing when to hit, stand, double down, or split is based on the rules and probabilities, not just guesswork.
-
Reduce the House Edge: By playing correctly according to blackjack basic strategy, you can bring the house edge down to as low as 0.5% in favorable rulesets.
-
Manage Your Bankroll: Understanding the game helps you avoid reckless bets and prolonged losing streaks by playing smart.
-
Enhance Enjoyment: A deeper understanding of the game makes it more engaging and rewarding.
Whether you're looking to learn blackjack rules fast for a quick game or delve into advanced strategies, a solid grasp of the foundational rules is indispensable. This classic game offers endless opportunities for strategic thinking and thrilling moments, making it a timeless favorite in both land-based and online casino settings. By mastering its rules, you're not just playing; you're strategizing your way towards a more successful and enjoyable blackjack experience.